- Definition of MAC (ADDRESS) - MAC (ADDRESS) stands for Media Access Control Address.
- MAC Address IP Address; 1. MAC Address stands for Media Access Control Address. IP Address stands for Internet Protocol Address. MAC Address is a six byte hexadecimal address. IP Address is either four byte (IPv4) or six byte (IPv6) address. A device attached with.

Each network-compatible device has at least one unique hardware ID – the media access control address (in short: MAC address). What this is all about and how you can find or rewrite the MAC address is explained below.
Technology MAC ADDRESS abbreviation meaning defined here. What does MAC ADDRESS stand for in Technology? Get the top MAC ADDRESS abbreviation related to Technology. There are three common technology definitions for MAC: (1) Short for Media Access Control. See MAC address or MAC layer. (2) When spelled Mac, the brand name and registered trademark for a line of computers from Apple Inc. See under Macintosh computer. (3) Short for Mandatory Access Control.
- What is a MAC address?
- Finding out your MAC address: a how-to guide
- Assigning the MAC address using software
What is a MAC address?
Each device that is integrated into a computer network requires a network adaptor. This adapter receives a worldwide unique identification number from the manufacturer: the MAC address. This enables devices like desktop computers, tablets, or mobile phones to be identified in the network and addressed as required. If a device has several network adapters (for example, for several LAN connections or different communication standards like Ethernet, WiFi, FDDI, Bluetooth, or Token Ring), a different address is available for each standard.
The MAC address (short for media access control address) is the worldwide unique hardware address of a single network adapter. The physical address is used to identify a device in computer networks.
Since MAC addresses are assigned directly by the hardware manufacturer, they are also referred to as hardware addresses. With Microsoft Windows, the MAC address is referred to as the physical address. Apple uses the terms Ethernet ID, Airport ID, or WiFi address, depending on the communication standard. The term device address, on the other hand, is fuzzy, since a device can have several network adapters and therefore different MAC addresses.
The MAC address in practice
Conflicting MAC addresses are a basic requirement for error-free network communication.
Data transmission in computer networks is a complex communication process in which different requirements including reliability, security, and efficiency must be met. This can be illustrated using the OSI models (abbreviation for open systems interconnection) – a reference model developed by the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) that maps network communication to 7 layers. During data transmission, each layer of the OSI model is run through on both the sender and receiver sides.
MAC addresses are used on the backup layer (layer 2) of the OSI model – actually, the media access controlsublayer introduced by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
In the extension of the OSI model designed by the IEEE, the backup layer (layer 2) is divided into the sublayers media access control (2a) and logical link control (2b).
The backup layer is located between the bit transfer layer (layer 1) and the switching layer (layer 3). While the bit transmission layer provides protocols and tools responsible for maintaining the physical connection, protocols on the backup layer control how different systems share the available transmission medium. Secure system connections are abstracted from the physical connection. The actual transmission of data packets takes place at the switching level via IP.
For example, if you want to send an IP packet over Ethernet, your computer transmits a data frame that is addressed to the target computer’s MAC address on the backup layer, according to the OSI model.
If the target computer is not in the local network, a router is addressed and instructed to forward it to the internet. Routers integrated into a social network also have a unique MAC address.
An Ethernet data frame contains information that is read out at different levels of the OSI model.
Data frames in IPv4 networks contain the following components:
- Destination address (destination computer MAC address)
- Source address (sender’s MAC address)
- Control information for data flow control
- User data (the data packet that needs to be transmitted later on the switching layer)
- Checksums that ensure data integrity
A target computer that receives a data frame first reads it on the backup layer and compares the target address of the frame with its own MAC address. If the addresses match, the target computer starts interpreting the frame at the next higher level.
Network devices that are only used to forward data packets (repeaters) or manage parts of the network (bridges and switches) usually do not actively participate in network communication and so do not require their own MAC addresses.
To link the address assignment on the backup layer with the address assignment on the switching layer, the address resolution protocol (ARP) is used in IPv4 networks. Each computer in the local network maintains an ARP table whereby IP addresses are assigned to MAC addresses.
ARP is vulnerable to an attack pattern called ARP spoofing. The danger of ARP spoofing and the countermeasures you can take are discussed in the article above.
What Mac Address Stands For What
The new internet protocol standard IPv6 uses the neighbor discovery protocol (NDP).
MAC address syntax
MAC addresses in LAN or WLAN networks consist of 6 bytes (48 bits) and are written in hexadecimal notation. The use of separators such as hyphens or colons between two bytes increases readability.
The following example shows the MAC address of a desktop computer in binary and hexadecimal format:
In our example, we use canonical representation of the bit sequence. This corresponds to the order in which MAC addresses are transmitted in Ethernet. Other communication standards like Token Ring provide for bit-reversed transmission, starting with the most significant bit.
The bit sequence of each MAC address is divided into 4 areas, each of which encodes different information.
- Bit 1 (receiver): The first bit of the MAC address specifies whether it is an individual or group address. This bit is called I/G (short for individual/group). If I/G = 0, it is a unicast address for a single network adapter. Multicast addresses are identified by I/G = 1 and are addressed to several receivers.
- Bit 2 (registry): The second bit of the MAC address indicates whether it is an address with global validity (universal) or whether the address has been assigned locally (local). The bit is called U/L. If U/L = 0, the address is valid worldwide as a universally administered address (UAA). Addresses that are only locally unique are called locally administered address (LAA) and are marked with U/L = 1.
- Bit 3–24 (manufacturer identification): Bits 3 to 24 encode an identifier (organizationally unique identifier, OUI), which is assigned exclusively to hardware manufacturers by IEEE. The assignment of OUIs is usually public and can be determined via databases. A corresponding service is available, for example, on aruljohn.com.
- Bit 25-48 (network adapter identifier): Bits 25 to 48 provide device manufacturers with 24 bits for assigning a unique hardware identifier (organizationally unique address, OUA). This means that 224 (= 16.777.216) unique OUAs can be assigned per OUI.
Table: Subareas of an MAC address
Label | I/G | U/L | OUI | OUA |
Bit | 1. | 2. | 3.–24. | 25.–48. |
Function | Recipient group | Awarding office | Manufacturer code | Network adapter identification |
Finding out your MAC address: a how-to guide
MAC addresses can be queried through the terminal in all modern operating systems with little effort – both on the local system and remotely in the network. The following table shows the corresponding command line commands for the most common operating systems.
Table: MAC address read out
| Operating system | Terminal command | Remote |
|---|---|---|
| FreeBSD | ifconfig | arp -a |
| NetBSD | ifconfig -a | arp -a |
| OpenBSD | ifconfig -a | arp -a |
| Linux | ip link | ip neigh |
| Mac OS X / macOS | ifconfig | arp -a |
| Solaris | ifconfig -a | arp -a |
| Windows XP Professional | getmac /v | arp -a |
| Windows (ab 2000) | ipconfig /all | arp -a |
On mobile devices, you can display the MAC address in the settings.
Table: Get MAC addresses on mobile devices
| Operating system | Local |
|---|---|
| Android | Settings > Phone Information > Hardware Information |
| Apple iOS | Settings > General > Info > WiFi address |
| Windows Phone 7 | Settings > Info > More Information |
Read MAC address locally
If you want to read out the MAC addresses of the LAN and WiFi adapters on your Windows computer, proceed as follows if using Windows 10.
Step 1: Open the terminal of your operating system. For example, use the keyboard shortcuts [Windows button]+[R]. Then enter “cmd” in the window “Run” and confirm with “OK.”
Step 2: From Windows 2000 onwards you can use the command line utility ipconfig with the “/all” option to get the MAC address of all network adapters on your Windows computer.
Alternatively get the MAC address with the command “getmac /v”

Step 3: With Windows, the MAC address is displayed under “physical address.”
Accessing your MAC address remotely
Thanks to ARP, in IPv4 networks it is possible to determine other devices’ MAC addresses in the same local network. With Windows and most unixoid operating systems, use the command line “arp” with the option to display you system’s ARP table in the terminal.
You will receive a terminal output according to the following scheme:
If you just want to read the MAC address of a specific network adapter remotely, use the command “arp –a” in a combination with the target adapter’s local IPv4 address.
Assigning the MAC address using software
MAC addresses are invariably assigned by device manufacturers and are “burned” into the network adapter chip on the hardware side. However, numerous operating systems offer the option to overwrite hardware addresses on the software side. This is referred to as spoofing. In this case, a system does not send the addressed adapter’s real network hardware address in network communication, but instead a user-defined MAC address.
Assigning an MAC address in Windows
With Windows, you can overwrite the MAC address through the device manager if the network adapter’s device driver supports this function.
Step 1: Open the network adapter settings. To do this, follow the click path: Start à Settings à Network and Internet à Ethernet à Change Adapter Options
Step 2: Right-click on the desired network adapter and select “Disable” in the context menu.
Step 3: Right-click on the desired network adapter and select “Properties” from the context menu. A pop-up window opens called “Network adapter properties.”
Step 4: Click on the “Configure” button in the pop-up window and select the “Locally Administered Address” property under “Advanced.” Enter your chosen software MAC address under “Value.”
Assign MAC address in unixoid operating systems
Unix derivatives such as Linux, macOS, Solaris, and the BSD operating systems support the assignment of MAC addresses through the terminal on the software side.
Table: Overwriting a MAC address
Operating system | Terminal command |
Linux | ip link set dev <Interface> addr XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX or ifconfig <Interface> promisc and finally ifconfig <Interface> hw ether XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX |
Mac OS X / macOS | ifconfig <Interface> ether XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX |
Solaris | ifconfig <Interface> ether XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX |
FreeBSD | ifconfig <Interface> link XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX |
NetBSD | ifconfig <Interface> link XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX activate |
OpenBSD | ifconfig <Interface> lladdr XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX |
We illustrate the procedure using the most commonly used Unix derivative: Linux. If you want to change your network adapter’s MAC address, proceed as follows.
Step 1: Open the operating system terminal – for example, with the key combination [CTRL]+[ALT]+[T].
Step 2: Determine the name and current MAC address of the desired network adapter. To do this, enter the following command in the command line:
Note the hardware address assigned by the manufacturer in case you want to undo the change.

Step 3: Turn off the network adapter by entering the following command in the command line:
Enter the name of the network adapter determined through “ip link” for <Interface>.
Step 4: Overwrite the network address assigned by the manufacturer with one of the options specified in the table.
Enter the chosen MAC address instead of XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
Step 5: Restart the network adapter. Use the following command line command:
To ensure that the selected network adapter is accessible at the MAC address you selected, re-read the network information with “ip link” (see step 1).
For starters, MAC Address stands for Media Access Control Address. It is used as a unique identifier for your device on network interfaces like wireless networks (Wi-Fi) and Ethernet connections. To further break it down: you know how network providers use your phone's IMEI number to identify your device on their networks, MAC address performs the same function but for all things internet-related.
These MAC addresses are built-in or burned-in addresses, and like IMEI numbers, no two devices have the same MAC address. That is why they are a very effective means of identifying devices on network interfaces. Their structure can get confusing.
In this article, we will walk you through some uses of MAC addresses for wireless network connectivity and how you can find the MAC addresses of your devices — mobile and PC.
Also on Guiding Tech
How to Find MAC, IP, and DNS Address on Windows 10
Read MoreUsing MAC Addresses
Primarily, MAC addresses are used to identify devices connected to your home or office network. While you can use device names to identify devices connected to your network, the MAC address is a more accurate identifier.
Say you have two friends over at your place, and their smartphones (iPhone X and OnePlus 7) are connected to your home internet. Blocking either of them might be difficult because both devices would not appear as iPhone X and OnePlus 7 on your router admin panel. Instead, they would be identified by a weird-looking combination of 12 alphanumeric characters grouped in twos by a colon or a hyphen.
So instead of seeing iPhone X or OnePlus 7 on your router dashboard, you will most likely see something like this: 23-78-98-A8-8P-6C or 75:8A:8B:48:12:54. These are typical formats for MAC addresses.
Another use-case of the MAC address is for unblocking a device from your Wi-Fi network. If you have numerous devices that you have blacklisted from your home or office internet, whitelisting a device would be difficult if you don't know its MAC address.
Additionally, if you have a router that lets you prioritize internet traffic by devices through Quality of Service (QoS) settings, knowing the MAC address of your devices is also important. That is because you can only add a device to the QoS rules or priority networks of your router using its MAC address.
Now that you know what a MAC address is, what it does, as well as it uses, check out how to identify the MAC addresses of your mobile phone and computer.
Finding MAC Addresses
1. How to Find MAC Address on Android
Step 1: Launch your device's Settings menu.
Step 2: Tap 'Network & Internet' option.
Step 3: Tap Wi-Fi.
Step 4: On the Wi-Fi settings menu, tap the name of the Wi-Fi device you are connected to. Alternatively, tap the gear icon.
Step 5: Tap the Advance drop-down button.
You should see your device's MAC address (under the Network details section).
2. How to Find MAC Address on Windows PC
Method 1
Step 1: Tap the Wi-Fi icon on the system tray/taskbar.
Step 2: On the network, you are connected to, tap Properties.
Step 3: Scroll to the bottom of the network settings page, and under the Properties section, you should see your computer's Wi-Fi MAC address.
Method 2
Step 1: Type in cmd into your Windows search bar and tap Command Prompt on the search result.
That launches the Command Prompt application in a new window.
Step 2: Type or paste this command ipconfig /all into the Command Prompt console and hit the Enter button.
That will display a bunch of network configurations in the console.
Step 3: Under the 'Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi' section, check for Physical address to see the Wi-Fi MAC address of your Windows computer.
3. How to Find MAC Address on iPhone or iPad
Step 1: Launch the Settings menu on your iPhone or iPad.
Step 2: Tap General.
Step 3: Tap About.
Step 4: Scroll to the bottom of the page and locate the Wi-Fi address. That is the MAC address of your iOS device.
4. How to Find MAC Address on Router's Admin Panel
You can also remotely check for MAC addresses of a device from the admin panel or dashboard of your Wi-Fi router.
Because there are several brands of routers, each with varying configurations and settings, we cannot provide accurate steps for checking MAC Addresses on your router's admin panel. We recommend that you check the device management section of your router. You should find a couple of devices connected to your Wi-Fi alongside their MAC addresses.
Note: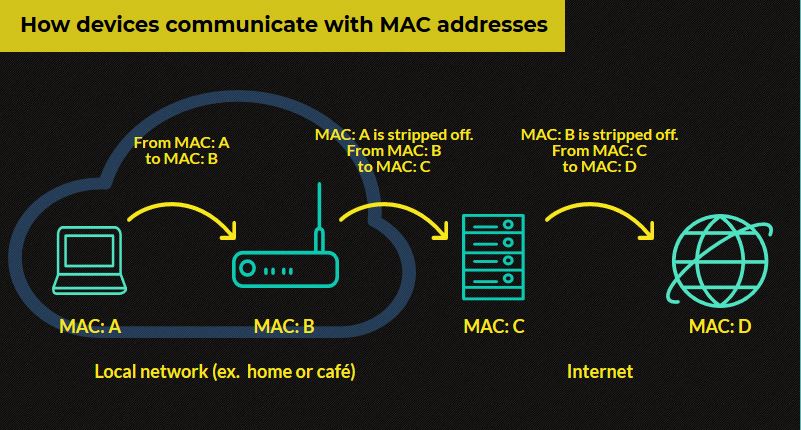 We also recommend checking the instruction manual or online documentation for your router on the manufacturer’s website to determine how to check connected devices and their MAC addresses.
We also recommend checking the instruction manual or online documentation for your router on the manufacturer’s website to determine how to check connected devices and their MAC addresses.Also on Guiding Tech
How to Change Your MAC Address on a PC or a Mac
Read MoreTake Control of Your Network
You can identify devices on your network using MAC addresses. On top of that, you can manage your network quality by filtering out unwanted devices, assigning better QoS settings, prioritizing traffic, etc. However, you can do all these effectively only if you know the MAC addresses of devices hooked to your network. Follow the steps above to check the MAC address of your Android and iOS phones as well as your Windows computer.
Next up: Ever wondered what an Internet Protocol address (IP address) is? We explained everything you need to know in the article linked below.
The above article may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. However, it does not affect our editorial integrity. The content remains unbiased and authentic.Read NextGT Explains: What is an IP Address and Difference Between a Static and Dynamic IP Address?Also See#iphone #network
Did You Know
Windows 10 is the last Windows since Microsoft is changing the approach of building and delivering OS.